Clipping Board » Medical Myths ─ The truth about healthcare is often different from what you intuitively think.
 【United Online Project / Excerpted and compiled from the book "Using Only Blood Pressure Medication Is a Death Wish"】
【United Online Project / Excerpted and compiled from the book "Using Only Blood Pressure Medication Is a Death Wish"】
2012.06.07 11:58 am
The world's most authoritative medical research journal, *The Lancet*, has pointed out that blood pressure medications can cause kidney damage. Studies show that patients with cardiovascular diseases or diabetes who use hypertension drugs long-term are significantly more likely to experience kidney function impairment, especially when the drugs are used in combination. The UK's *British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology* further states that when combined with anti-inflammatory drugs (such as aspirin or acetaminophen), severe irreversible kidney failure can occur within just three months.
Blood pressure medications have rapidly become one of the most "popular" drugs over the past 20–30 years and rank as the most commonly prescribed medication in many countries. While they quickly and effectively lower blood pressure, how exactly do these drugs "viciously" harm our body's crucial filtration system—the kidneys?
### Reasons Blood Pressure Medications Cause Kidney Failure
Most standard blood pressure medications used to address kidney failure are primarily angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I). These drugs not only block downstream signals released by the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidneys, keeping small arteries in a non-contracted state, but also prevent the breakdown of bradykinin, a vasodilating factor naturally secreted by the body. This leads to further vasodilation.
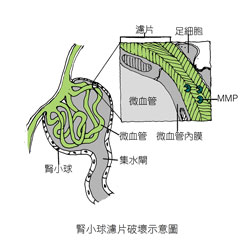
Image provided by Microscope Culture
However, bradykinin significantly increases capillary permeability (meaning leakage occurs), allowing larger substances (such as proteins) that shouldn't normally leak out to escape from blood vessels. This triggers an inflammatory response, prompting the body to send antibodies and immune cells to attack the inflamed area. Additionally, fibrous tissue rapidly proliferates to encapsulate the region, causing many glomerular filtration membranes to thicken and lose their filtering function.
Even worse, when cells around the glomerulus become hypoxic due to thickened filtration membranes—much like a person whose nose and mouth are blocked and unable to breathe—they desperately secrete enzymes (such as MMPs) designed to break down fibers, tearing the "filtration membranes" full of holes in search of an exit. This allows large molecules in the blood (such as proteins) to easily leak into the urine, a phenomenon commonly known as proteinuria. This is likely the main reason why using angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors alone can lead to a 4.2-fold increase in end-stage kidney failure within three years!
### Combining Blood Pressure Medications Accelerates the Need for Dialysis
Image provided by Microscope Culture
If only angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I) were used, it might be manageable. However, when combined long-term with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), another potent blood pressure medication, the effect is akin to suddenly releasing a slightly tightened hose used to regulate water flow: the water pressure and volume naturally drop. Similarly, when small arteries throughout the body are repeatedly forced to dilate, pressure and blood flow plummet sharply. This causes the juxtaglomerular apparatus to continuously release renin without receiving a response. The blood pressure in the glomerular capillaries becomes insufficient to generate the osmotic pressure needed to pass through the "filtration membranes," leading to a significant reduction in urine output. The cells downstream of the nephron also end up in a hypoxic state.Life often finds a way when all seems lost! When the pressure signals released by the kidneys are constantly intercepted by antihypertensive drugs, causing waste products like uric acid, urea, and creatinine to accumulate in the body, the body, in order to survive, secretes a large amount of a "scissor-hand" enzyme called MMP. This enzyme punches holes in the collagen "filter," allowing these waste products to be excreted more quickly. However, this method also leads to the loss of proteins in the blood, resulting in foamy or cloudy urine, or even hematuria! There’s no doubt about it—kidney function is rapidly declining!
Combining Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Raises Kidney Alarms

Image provided by Microscope Culture
Heaven’s wrath can be avoided, but man’s folly is unforgivable! Most people with poor cardiovascular function, in addition to long-term use of antihypertensive drugs, also take antiplatelet medications like aspirin or anti-inflammatory drugs such as acetaminophen (e.g., Tylenol) to prevent strokes and myocardial infarction. These drugs are essentially nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which work by inhibiting the secretion of prostaglandins in cells, thereby preventing platelet aggregation and reducing inflammation.
However, the kidneys rely on prostaglandin stimulation to secrete renin. NSAIDs effectively suppress prostaglandins, leading to a significant reduction in renin secretion and preventing arterioles from constricting. When combined with antihypertensive drugs, this results in blood pressure dropping so low in the glomeruli that it becomes insufficient to filter the blood. To survive, the body resorts to the aforementioned method, which only accelerates kidney damage, leading to irreversible kidney failure! This condemns one to a lifetime of dialysis...
[This article is excerpted from Dr. Chen Zhiming’s 2012 book *Relying Solely on Antihypertensive Drugs Is a Death Wish*, published by Microscope Culture.]
Source: http://udn. com/ NEWS/ NATIONAL/ AD2/ 7143856. shtml#ixzz1x7lNkwgs
Long-term Blood Pressure Meds May Lead to Early Kidney Failure


2012.06.07 11:58 am
The world's most authoritative medical research journal, *The Lancet*, has pointed out that blood pressure medications can cause kidney damage. Studies show that patients with cardiovascular diseases or diabetes who use hypertension drugs long-term are significantly more likely to experience kidney function impairment, especially when the drugs are used in combination. The UK's *British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology* further states that when combined with anti-inflammatory drugs (such as aspirin or acetaminophen), severe irreversible kidney failure can occur within just three months.
Blood pressure medications have rapidly become one of the most "popular" drugs over the past 20–30 years and rank as the most commonly prescribed medication in many countries. While they quickly and effectively lower blood pressure, how exactly do these drugs "viciously" harm our body's crucial filtration system—the kidneys?
### Reasons Blood Pressure Medications Cause Kidney Failure
Most standard blood pressure medications used to address kidney failure are primarily angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I). These drugs not only block downstream signals released by the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidneys, keeping small arteries in a non-contracted state, but also prevent the breakdown of bradykinin, a vasodilating factor naturally secreted by the body. This leads to further vasodilation.

Image provided by Microscope Culture
However, bradykinin significantly increases capillary permeability (meaning leakage occurs), allowing larger substances (such as proteins) that shouldn't normally leak out to escape from blood vessels. This triggers an inflammatory response, prompting the body to send antibodies and immune cells to attack the inflamed area. Additionally, fibrous tissue rapidly proliferates to encapsulate the region, causing many glomerular filtration membranes to thicken and lose their filtering function.
Even worse, when cells around the glomerulus become hypoxic due to thickened filtration membranes—much like a person whose nose and mouth are blocked and unable to breathe—they desperately secrete enzymes (such as MMPs) designed to break down fibers, tearing the "filtration membranes" full of holes in search of an exit. This allows large molecules in the blood (such as proteins) to easily leak into the urine, a phenomenon commonly known as proteinuria. This is likely the main reason why using angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors alone can lead to a 4.2-fold increase in end-stage kidney failure within three years!
### Combining Blood Pressure Medications Accelerates the Need for Dialysis

Image provided by Microscope Culture
If only angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I) were used, it might be manageable. However, when combined long-term with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), another potent blood pressure medication, the effect is akin to suddenly releasing a slightly tightened hose used to regulate water flow: the water pressure and volume naturally drop. Similarly, when small arteries throughout the body are repeatedly forced to dilate, pressure and blood flow plummet sharply. This causes the juxtaglomerular apparatus to continuously release renin without receiving a response. The blood pressure in the glomerular capillaries becomes insufficient to generate the osmotic pressure needed to pass through the "filtration membranes," leading to a significant reduction in urine output. The cells downstream of the nephron also end up in a hypoxic state.Life often finds a way when all seems lost! When the pressure signals released by the kidneys are constantly intercepted by antihypertensive drugs, causing waste products like uric acid, urea, and creatinine to accumulate in the body, the body, in order to survive, secretes a large amount of a "scissor-hand" enzyme called MMP. This enzyme punches holes in the collagen "filter," allowing these waste products to be excreted more quickly. However, this method also leads to the loss of proteins in the blood, resulting in foamy or cloudy urine, or even hematuria! There’s no doubt about it—kidney function is rapidly declining!
Combining Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Raises Kidney Alarms

Image provided by Microscope Culture
Heaven’s wrath can be avoided, but man’s folly is unforgivable! Most people with poor cardiovascular function, in addition to long-term use of antihypertensive drugs, also take antiplatelet medications like aspirin or anti-inflammatory drugs such as acetaminophen (e.g., Tylenol) to prevent strokes and myocardial infarction. These drugs are essentially nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which work by inhibiting the secretion of prostaglandins in cells, thereby preventing platelet aggregation and reducing inflammation.
However, the kidneys rely on prostaglandin stimulation to secrete renin. NSAIDs effectively suppress prostaglandins, leading to a significant reduction in renin secretion and preventing arterioles from constricting. When combined with antihypertensive drugs, this results in blood pressure dropping so low in the glomeruli that it becomes insufficient to filter the blood. To survive, the body resorts to the aforementioned method, which only accelerates kidney damage, leading to irreversible kidney failure! This condemns one to a lifetime of dialysis...
[This article is excerpted from Dr. Chen Zhiming’s 2012 book *Relying Solely on Antihypertensive Drugs Is a Death Wish*, published by Microscope Culture.]
Source: http://udn. com/ NEWS/ NATIONAL/ AD2/ 7143856. shtml#ixzz1x7lNkwgs

